Rethinking Talent Strategy in the Age of AI: How to Align Roles, Structure, and Salary in a Changing Workforce
Executive Summary
Think AI adoption will cut your labor costs? The reality is more complex. The problem isn't the technology but the misconception that AI equals a cheaper workforce.
AI isn't eliminating jobs; it's transforming them into higher-value hybrid roles that command premium salaries. Meanwhile, regulatory complexity is increasing, and skilled workers are approaching retirement, creating a dual challenge for organizations. Those still hoping AI will reduce payroll costs are setting themselves up for competitive disadvantage.
Unertanding the AI Shift in the Workforce
The misconception: AI is replacing jobs.
The reality is: AI is reshaping tasks, responsibilities, and expectations.
Like C-3PO from Star Wars, AI is a helpful assistant, but it's flawed, misinterprets context, and needs human guidance.
The pace of AI adoption has been unprecedented. 78 percent of organizations now use AI in at least one business function, up from 55 percent a year earlier.1 This rapid implementation is creating new workforce dynamics that most companies haven't fully grasped.
While businesses rush to adopt AI tools, they're slower to adapt their workforce strategies. Most organizations haven't formally acknowledged this shift:
· Job descriptions remain outdated
· Compensation is tied to tasks that no longer reflect current workflows
· Performance metrics don't account for AI collaboration
The disconnect between technology adoption and talent strategy is creating competitive gaps. Companies that understand AI's true impact on work aren't just implementing tools. They're rethinking how roles function and what skills command premium pay.
Strategic Role Framework: The 80/20 AI Adoption Model
Most companies are struggling with AI implementation. Just 25 percent of AI initiatives in recent years have lived up to ROI expectations, while organizations have achieved enterprise-wide rollouts with only 16 percent of AI projects. Nearly two-thirds of CEOs acknowledge that the fear of missing out drives investment in new technologies before they have a clear understanding of its value.2
Despite these challenges, the trend isn't reversing. Over the next three years, 92 percent of companies plan to increase their AI investments.3 The solution isn't less AI but a smarter implementation through strategic role design.
There are two approaches to structuring AI-augmented roles:
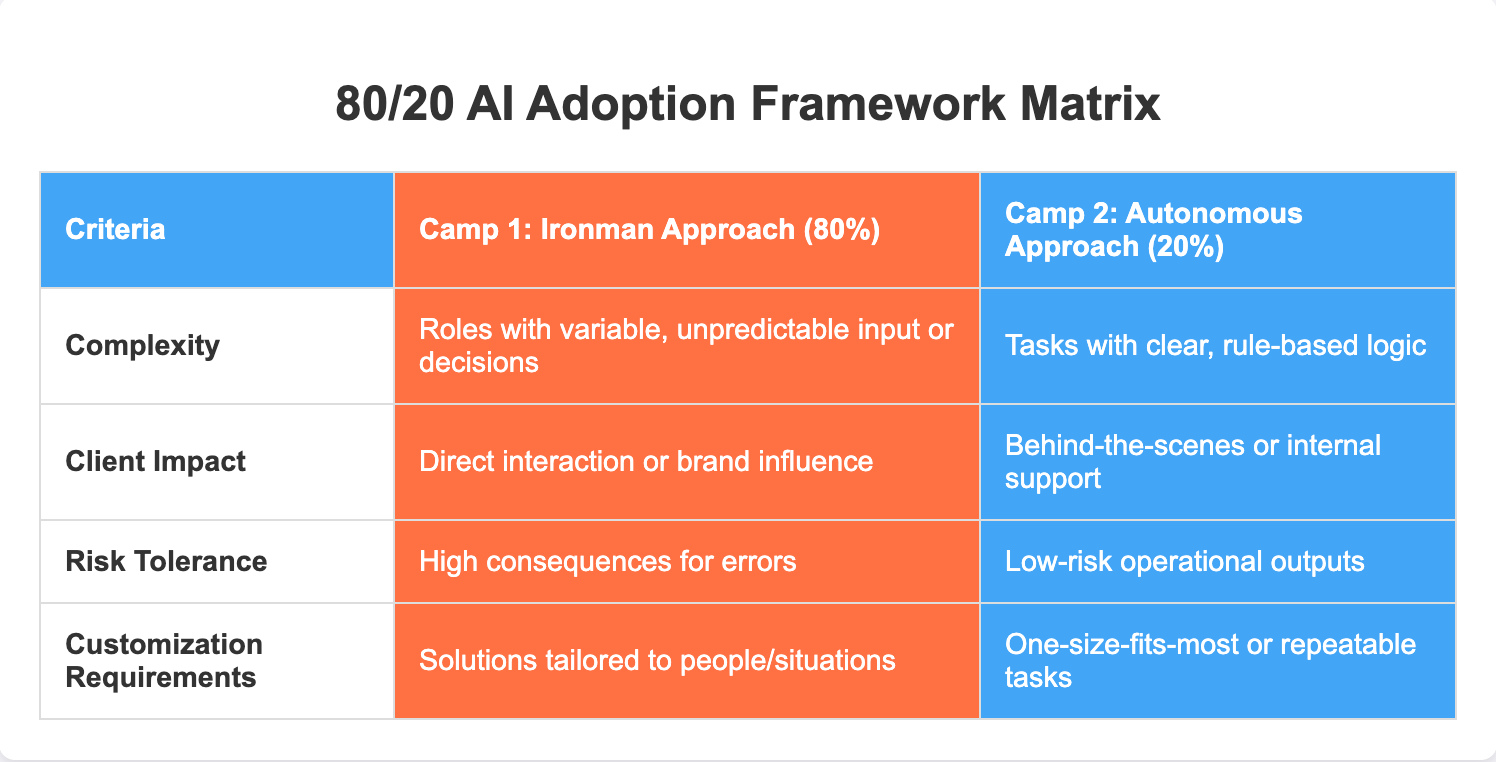
Camp 1: The Ironman Approach (80%)
Like Tony Stark's suit, AI becomes a powerful extension of human capability. These are human-led roles that are augmented by AI tools. Ideal for work requiring critical thinking, contextual understanding, judgment, or client-facing roles. AI supports the person but doesn't drive outcomes autonomously.
Examples:
· Skilled trades using AI-powered diagnostics
· Call center reps handling escalations beyond bot's scope
· Project managers using AI to assist reporting, not replace leadership
· Administrative professionals coordinating across AI outputs
Camp 2: The Autonomous Approach (20%)
Here, AI takes the lead while humans provide oversight. These are AI-led roles with minimal human validation and reactive oversight. Suitable for repetitive, well-defined, high-volume, low-risk tasks.
Examples:
· Initial resume screening
· Tier-1 call center chatbot responses
· Routine data entry or routing
· Reporting dashboards updated by AI, reviewed by team leads
Why the 80/20 Split Works
This distribution reflects market reality. Most work still requires human judgment, creativity, and relationship management—areas where AI excels as a tool but struggles as a replacement. The 20 percent autonomous allocation captures routine tasks that AI can handle reliably while acknowledging that even "simple" processes often need human oversight.
The split also provides flexibility. As AI capabilities improve, some Camp 1 roles may shift toward Camp 2, but the human element remains critical for complex decision-making, client relationships, and managing unexpected situations that AI can't navigate independently.
Role Assignment Criteria
Use the following criteria to evaluate where each role belongs:
When to Reassess Camp Assignment:
· Quality drops or output inconsistencies
· Team inefficiencies or operational delays
· Negative client or user feedback
· New tools or updated AI capabilities
Role Evolution & Salary Insights by Sector
The financial impact of AI adoption varies significantly by implementation approach. While 9 percent of companies report revenue increases of more than 5 percent from AI, another 39 percent see moderate increases of 1 to 5 percent. However, only 23 percent see AI delivering any favorable change in costs.4 This reinforces that AI's value lies in revenue enhancement and capability expansion, not cost reduction.
While AI transformation is occurring across all industries, the following examples from select sectors illustrate common patterns that organizations can apply to their specific contexts:
Call Centers
The transformation of customer service represents one of the most visible examples of AI reshaping traditional roles.
What's Changing:
AI chatbots and automated systems now handle routine inquiries like password resets, account balance checks, and basic product questions, managing the majority of initial customer contacts
Human agents focus on complex problem-solving, managing upset customers who escalated past AI systems, and retention conversations that require empathy, negotiation skills, and relationship building
Salary Impact:
· Tier-1 roles handling basic inquiries are plateauing or declining as AI takes over these functions
· Escalation specialists, customer experience leads, and hybrid AI-operations roles are seeing increased demand and premium pay due to their specialized skill sets
Skilled Trades & Manufacturing
Manufacturing floors and trade work are experiencing a technological integration that enhances rather than replaces human expertise.
What's Changing:
Equipment operators now work alongside AI-powered machinery that provides real-time diagnostics, predictive maintenance alerts, and performance optimization suggestions
Routine maintenance has evolved to include AI system monitoring, sensor calibration, and troubleshooting intelligent systems that can self-diagnose but require human interpretation and action
Salary Impact:
· Technicians who can interpret AI diagnostics and work with smart systems command significantly higher wages than those limited to traditional manual processes
· Entirely new roles like automation technicians and predictive maintenance specialists are emerging with competitive compensation packages that reflect their specialized knowledge
The following compensation data demonstrates these AI-driven salary shifts across key sectors, showing 2025 baseline salaries and projected 2026 increases as organizations compete for AI-fluent talent.
Insert Comprehensive Salary Data Table here. See here: Salary Guide Master Sheet.xlsx
Implementation Roadmap: How to Apply This Guide Internally
The regulatory landscape around AI is evolving rapidly, with U.S. federal agencies introducing 59 AI-related regulations in 2024; more than double the number in 2023 and issued by twice as many agencies.5 This growing complexity makes strategic implementation even more critical.
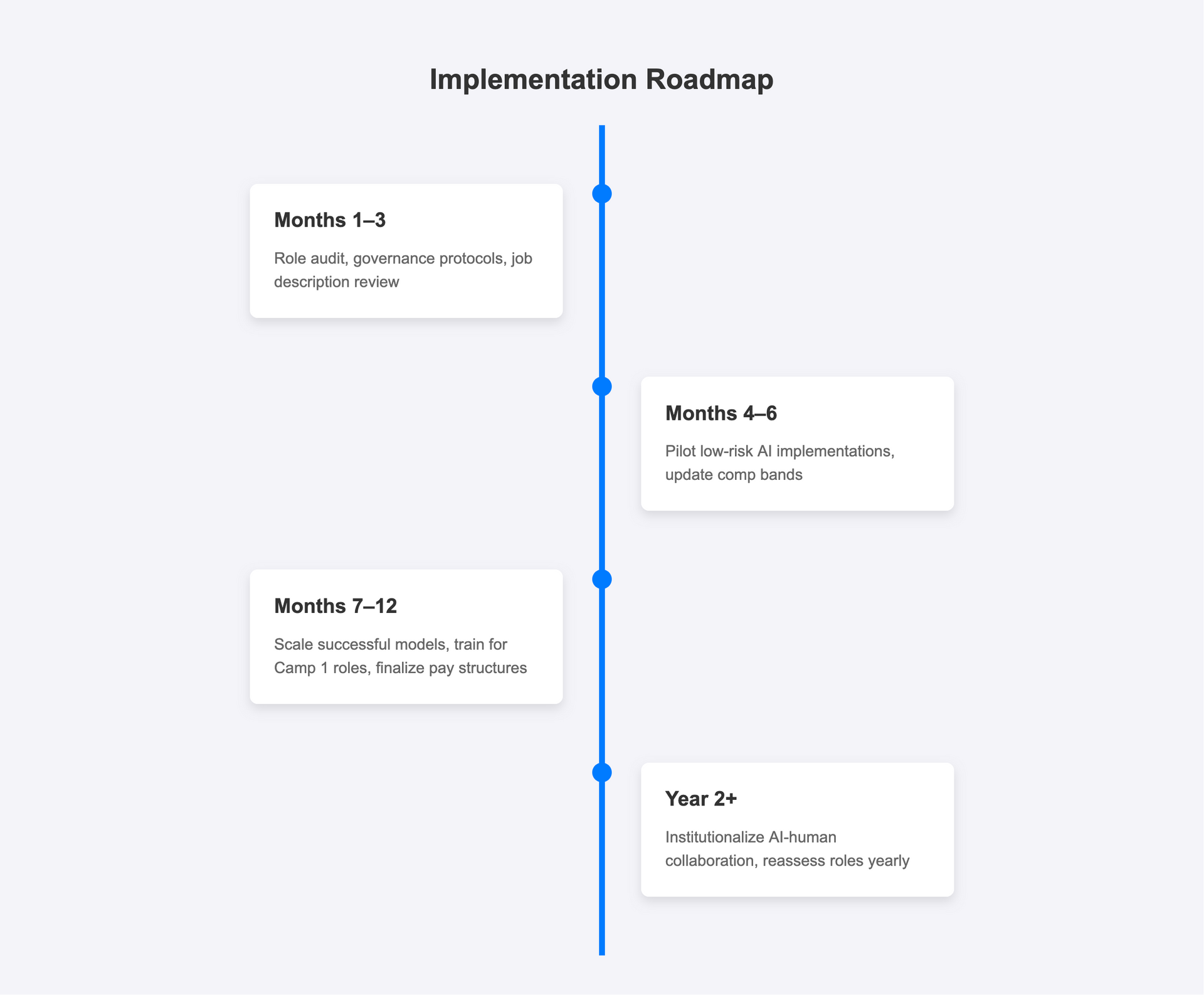
Months 1–3: Role audit, governance protocols, job description review
Begin by conducting a comprehensive audit of your current roles using the 80/20 framework criteria. Identify which positions fall into Camp 1 (Ironman) versus Camp 2 (Autonomous) categories. Simultaneously, establish governance protocols to ensure compliance with emerging AI regulations and begin updating job descriptions to reflect AI-augmented responsibilities.
Months 4–6: Pilot low-risk AI implementations, update comp bands
Launch pilot programs with Camp 2 roles first, as these involve lower risk and clearer implementation paths. Use these pilots to gather data on productivity changes and role evolution. Begin adjusting compensation bands based on your sector analysis and market research for AI-augmented positions.
Months 7–12: Scale successful models, train for Camp 1 roles, finalize pay structures
Expand successful pilot programs while beginning more complex Camp 1 implementations that require extensive training and change management. Focus on upskilling existing employees for hybrid roles rather than wholesale replacement. Finalize new compensation structures that reflect the premium value of AI-fluent workers.
Year 2+: Institutionalize AI-human collaboration, reassess roles yearly
Establish regular assessment cycles to evaluate role assignments as AI capabilities evolve. Build ongoing training programs to maintain your workforce's AI fluency. Create feedback loops to continuously refine your approach based on performance data and regulatory changes.
Governance & Risk Management
Effective AI implementation requires robust oversight to prevent costly mistakes and ensure consistent application across your organization.
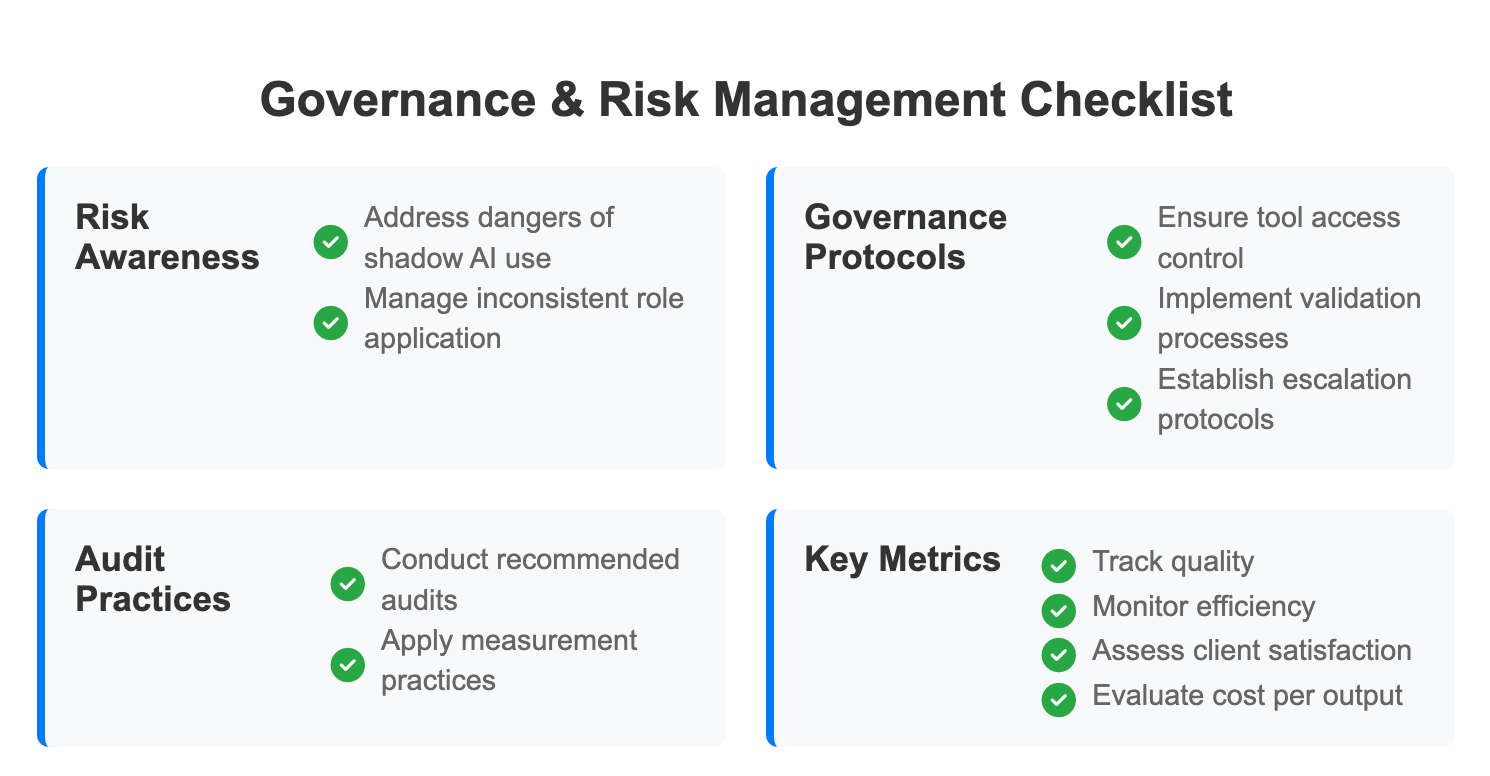
Dangers of shadow AI use and inconsistent role application.
When employees adopt AI tools without proper oversight, organizations face significant risks including data breaches, inconsistent outputs, and compliance violations. Departments implementing different AI approaches create operational silos that undermine the strategic benefits of coordinated AI adoption.
Governance must cover tool access, validation, and escalation protocols.
Establish clear policies for which AI tools employees can use, how outputs should be validated before implementation, and when human intervention is required. Create escalation pathways for situations where AI recommendations conflict with business judgment or regulatory requirements.
Recommended audit and measurement practices.
Implement regular reviews of AI tool usage, output quality, and role performance across both Camp 1 and Camp 2 positions. Document decision-making processes that involve AI recommendations to ensure accountability and enable continuous improvement.
Metrics to track: quality, efficiency, client satisfaction, cost per output
Monitor these key performance indicators to assess whether your AI integration is delivering expected results and identify areas needing adjustment before they impact business performance.
Bridging the Governance Gap: Action Steps for Employers and Job Seekers
Understanding AI's impact on roles is only the first step; successful implementation requires concrete action from both organizations and individuals navigating this transition.
For Employers:
· Identify top 5 roles most impacted by AI within your organization using the framework criteria outlined earlier
· Update job descriptions and salary bands to reflect AI-augmented responsibilities and market premiums for hybrid skills
· Train existing staff for hybrid functions rather than assuming you'll need to replace entire teams
· Partner with Allied OneSource for job description design, AI strategy support, and staffing solutions that align with your governance framework
For Job Seekers:
· Understand how your specific role is evolving within the AI landscape and whether it falls into Camp 1 or Camp 2 categories
· Build complementary skills that enhance your value in AI-era work, focusing on areas where human judgment remains critical
· Position yourself for emerging hybrid roles by developing both technical AI fluency and the soft skills that AI cannot replicate
· Evaluate potential employers' AI governance maturity to ensure you're joining organizations with sustainable, strategic approaches to AI integration
Rethink Talent Strategy, Hire for the Future
AI has changed the rules of work across every sector. The traditional approach of reactive hiring and static job descriptions no longer meets the demands of an AI-augmented workplace.
Employers can't afford to apply old job structures to a new reality. The organizations thriving in this transition are those investing in premium talent now, not those hoping AI will reduce their workforce costs.
Smart organizations will rethink job design, role expectations, and compensation now before growth or turnover exposes the cracks in their outdated talent strategies.
Allied OneSource can help:
As organizations navigate this AI transformation, having the right staffing partner becomes critical. Allied OneSource specializes in identifying talent that can thrive in AI-augmented environments and helping companies structure roles for this new reality.
· Review and realign job descriptions to accurately reflect AI-era role requirements and responsibilities
· Provide market intelligence on compensation shifts needed to attract and retain AI-fluent talent in your industry
· Source and place candidates who possess both traditional skills and the AI fluency needed for hybrid roles
References
1. Mayer, Hannah, and Lareina Yee. Superagency in the Workplace: Empowering People to Unlock AI’s Full Potential. McKinsey & Company, 28 Jan. 2025, https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/superagency-in-the-workplace-empowering-people-to-unlock-ais-full-potential-at-work.
2. Gross, Grant, Michael Chui, and Roger Roberts. “What ROI? AI Misfires Spur CEOs to Rethink Adoption.” CIO, 29 May 2025, https://www.cio.com/article/3996256/what-roi-ai-misfires-spur-ceos-to-rethink-adoption.html.
3., 4. McKinsey & Company. The State of AI: How Organizations Are Rewiring to Capture Value. 12 Mar. 2025, https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/quantumblack/our-insights/the-state-of-ai.
5. The 2025 AI Index Report. Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI), https://hai.stanford.edu/ai-index/2025-ai-index-report.











